Elastometric Bearing Design Spreadsheet
1 February 2025Table of Contents
Elastometric Bearing Design Spreadsheet
Elastomeric bearings play a crucial role in modern bridge and structural engineering, allowing controlled movement and load distribution between superstructures and substructures. These flexible yet durable components absorb vibrations, accommodate thermal expansion, and reduce stress on supporting structures.
In this guide, we’ll explore elastomeric bearing design principles, AASHTO standards, material specifications, and installation best practices to help engineers ensure optimal performance and compliance.
What is an Elastomeric Bearing?
An elastomeric bearing is a structural component made of reinforced neoprene or natural rubber, designed to support loads, allow movement, and reduce stress between structural elements. They are commonly used in:
✅ Bridge bearings
✅ Highway overpasses
✅ Railway structures
✅ Building foundations
These bearings accommodate horizontal movements and rotations while ensuring load transfer between structural components.
Key Features of Elastomeric Bearings
🔹 Flexibility & Load Distribution – Absorbs movement and evenly distributes structural loads.
🔹 Durability & Weather Resistance – Resists aging, extreme temperatures, and environmental exposure.
🔹 Low Maintenance – Requires minimal upkeep compared to mechanical bearings.
🔹 Cost-Effective Solution – More affordable than pot or spherical bearings while offering high performance.
Types of Elastomeric Bearings
There are two primary types of elastomeric bridge bearings:
1. Plain Elastomeric Bearings
- Composed entirely of high-grade rubber
- Best for light to moderate loads and small structural movements
2. Laminated (Reinforced) Elastomeric Bearings
- Consist of rubber layers reinforced with steel plates
- Suitable for higher loads and significant movements
- Improve compressive strength and stability
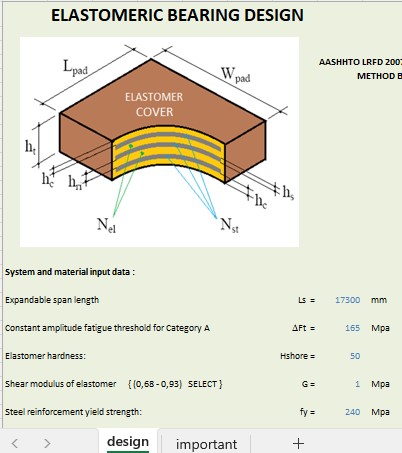
Elastomeric Bearing Design According to AASHTO Standards
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) provides guidelines for designing elastomeric bridge bearings, ensuring structural integrity and performance.
1. Load Capacity & Stress Analysis
- Dead Load & Live Load Considerations
- Axial, Shear, and Rotational Movements
- Thermal Expansion & Contraction Allowances
2. Material Selection
- Rubber Hardness (Durometer Shore A scale) – Typically 50-70 Shore A
- Steel Reinforcement for Laminated Bearings
- UV, Ozone & Weather Resistance
3. Thickness & Shape Optimization
- Bearing thickness affects flexibility and movement absorption.
- Rectangular or circular designs are selected based on load distribution requirements.
4. Installation & Maintenance Guidelines
- Proper placement to ensure even load distribution.
- Regular inspections to check for cracks, deformations, and aging.
- Lubrication & Cleaning in high-dust environments.
Advantages of Using Elastomeric Bearings
✅ Efficient Load Transfer – Ensures structural stability.
✅ Absorbs Vibrations – Reduces stress on bridges and buildings.
✅ Weather & Temperature Resistant – Performs well in extreme conditions.
✅ Cost-Effective & Low Maintenance – Long-lasting and economical.
Common Applications of Elastomeric Bearings
🛣️ Bridge Construction – Allows smooth expansion and contraction.
🏗️ High-Rise Buildings – Provides stability under seismic loads.
🚝 Railway Infrastructure – Reduces vibrations and structural stress.
🏛️ Industrial Facilities – Supports heavy machinery foundations.
Download the Elastomeric Bearing Design Spreadsheet
We’ve created a comprehensive Elastomeric Bearing Design Spreadsheet based on AASHTO standards, helping engineers quickly calculate load capacities, movement allowances, and material specifications.
📥 Download Now and streamline your elastomeric bearing design process today!