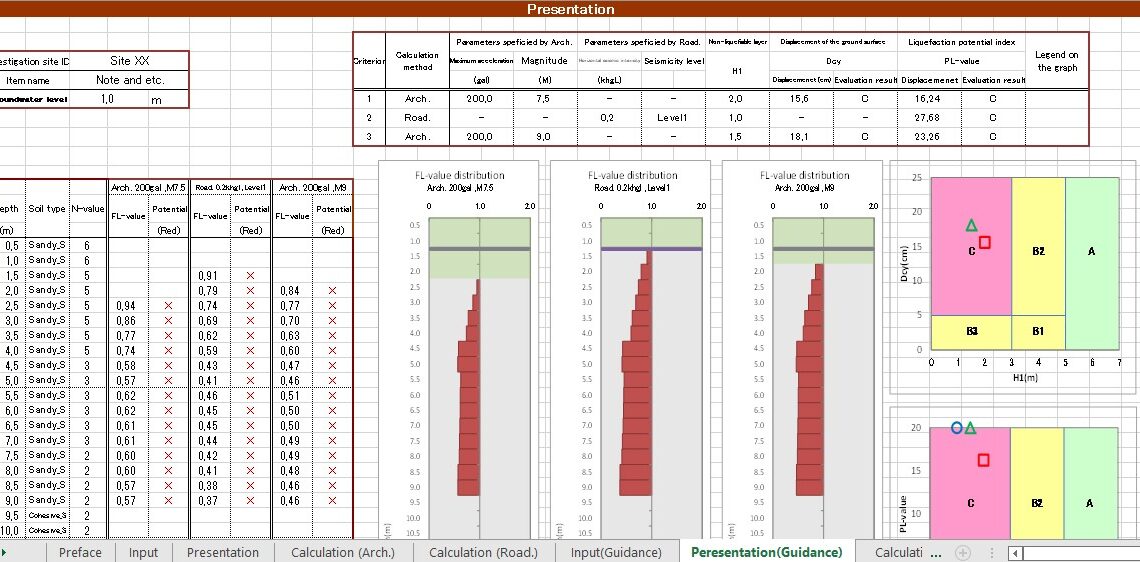
Analysis Tool On Soil Liquefaction Potential Spreadsheet
3 January 2025Table of Contents
Analysis Tool On Soil Liquefaction Potential Spreadsheet
Soil liquefaction is a phenomenon that occurs when saturated, loosely packed soils lose their strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress, such as an earthquake. This process can have devastating consequences, particularly in regions with seismic activity. In this article, we’ll explore what soil liquefaction is, why it happens, its impact, and how it can be mitigated.
What is Soil Liquefaction?
Soil liquefaction is a geotechnical phenomenon that transforms solid ground into a liquid-like state. It typically occurs in saturated, sandy soils under the pressure of rapid, cyclic loading, like that caused by an earthquake. When this happens, the soil particles rearrange, and the water pressure between the particles increases, reducing the soil’s ability to support structures.
Causes of Soil Liquefaction
Several factors contribute to soil liquefaction, including:
- Saturated Soils: Liquefaction mainly occurs in soils that are fully saturated with water, such as sandy or silty soils near rivers, lakes, or coastal areas.
- Loose Soil Structure: Loosely packed soil particles are more prone to rearrangement when subjected to stress.
- Seismic Activity: Earthquakes provide the rapid, cyclic loading necessary to destabilize soil structures.
- Groundwater Table: A high groundwater table increases the likelihood of liquefaction as it saturates the soil layers.
Effects of Soil Liquefaction
The consequences of soil liquefaction can be catastrophic, especially in urban areas:
- Structural Damage: Buildings, bridges, and roads can sink, tilt, or collapse as the ground loses its load-bearing capacity.
- Infrastructure Failures: Underground pipelines, utility lines, and sewage systems are often severely damaged.
- Economic Loss: Repairs and rebuilding after liquefaction-related damages can be costly, impacting local economies.
- Loss of Life: In extreme cases, liquefaction can lead to fatalities due to collapsing structures and ground instability.
Famous Examples of Soil Liquefaction
Soil liquefaction has been responsible for significant damage during many earthquakes. Notable examples include:
- The 1964 Niigata Earthquake in Japan, which caused widespread building collapses and ground failure.
- The 1989 Loma Prieta Earthquake in California, where liquefaction damaged highways and infrastructure.
- The 2011 Christchurch Earthquake in New Zealand, where extensive liquefaction led to severe property damage.
Mitigation Strategies for Soil Liquefaction
Preventing soil liquefaction requires a combination of engineering and geotechnical solutions. Here are some effective strategies:
- Soil Improvement Techniques: Methods like compaction, soil densification, and grouting can increase soil strength and reduce susceptibility to liquefaction.
- Drainage Systems: Installing drainage systems helps lower the groundwater table, reducing soil saturation.
- Structural Reinforcement: Designing buildings and infrastructure to withstand potential liquefaction effects can minimize damage.
- Geotechnical Studies: Conducting thorough soil analyses before construction helps identify areas at risk of liquefaction.
- Land Use Planning: Avoiding construction in high-risk areas can significantly reduce the impact of liquefaction.
Why Understanding Soil Liquefaction Matters
As urban areas expand and seismic risks increase, understanding soil liquefaction is more critical than ever. Engineers, city planners, and policymakers must work together to identify vulnerable regions and implement strategies to mitigate risks.
By investing in research, innovative technologies, and proper land management, we can minimize the devastating effects of soil liquefaction and create safer, more resilient communities.
Final Thoughts
Soil liquefaction is a hidden danger that can surface during earthquakes, causing extensive damage to infrastructure and human lives. However, with proactive measures and a deep understanding of this phenomenon, its impacts can be significantly mitigated.
If you’re a homeowner, engineer, or city planner, staying informed about soil liquefaction risks and solutions is essential. Share this article to spread awareness and encourage preparedness in your community.