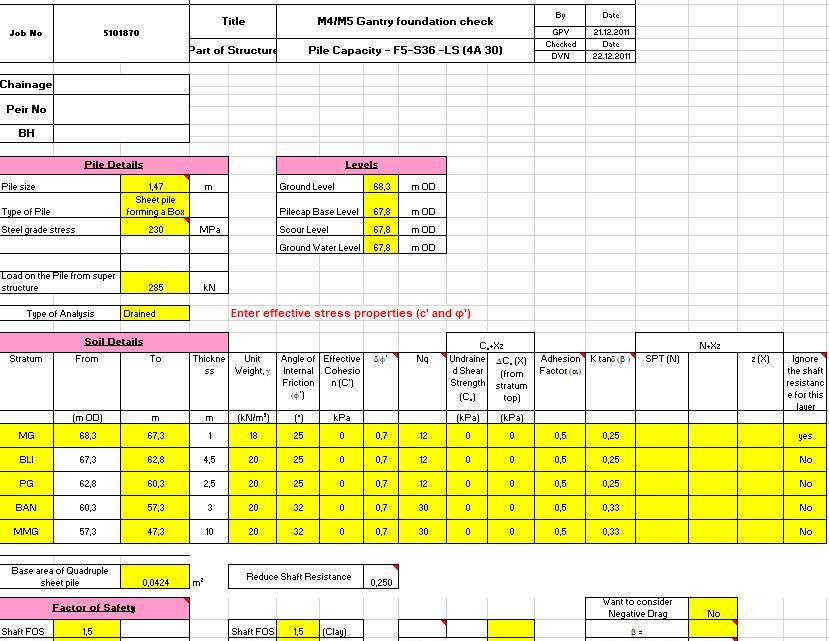
Box Pile Design Calculations Spreadsheet
1 May 2022Table of Contents
Box Pile Design Calculations Spreadsheet
When it comes to ensuring the stability of a structure, foundations play a critical role. Among the various foundation techniques, the box pile stands out for its versatility and reliability in construction. Whether you’re building a skyscraper, a bridge, or a residential property, box piles are often the unsung heroes providing the essential support needed to keep structures safe and stable. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of box piles, their applications, and why they’re a preferred choice in modern construction.
What is a Box Pile?
A box pile is a type of foundation element used in construction to transfer the load of a structure to deeper, more stable soil layers or bedrock. Unlike traditional piles, box piles are hollow, rectangular, or square in cross-section. This unique design allows them to handle substantial loads while being lightweight and cost-effective.
Box piles are typically made of reinforced concrete or steel, and their modular nature makes them easy to transport and install. Their hollow structure can also be filled with concrete or other materials to enhance strength when required.
Advantages of Box Piles
Box piles are increasingly popular in construction due to their numerous advantages:
- Load-Bearing Capacity: The design of box piles allows for excellent load distribution, making them suitable for heavy structures.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Their lightweight design reduces transportation and material costs compared to solid piles.
- Ease of Installation: Modular components simplify the installation process, saving time and labor on-site.
- Versatility: Box piles can be used in a variety of soil conditions, including soft, loose, or uneven terrain.
- Durability: Made from reinforced materials, box piles are resistant to corrosion and environmental degradation.
Applications of Box Piles in Construction
Box piles are used across a wide range of construction projects. Some common applications include:
1. Building Foundations
Box piles provide the necessary support for buildings, especially in areas with poor surface soil. They transfer the weight of the structure to deeper, more stable layers.
2. Bridge Construction
For bridges, where stability over water or uneven terrain is critical, box piles are an ideal choice. Their ability to resist lateral forces makes them essential in such projects.
3. Marine Structures
In harbors, piers, and other marine applications, box piles are favored for their ability to withstand the challenges posed by water and shifting soil.
4. Retaining Walls
Box piles can be used as part of retaining wall systems to hold back soil and prevent erosion, particularly in sloped areas.
Installation Process
The installation of box piles involves several key steps:
- Site Preparation: The site is surveyed, and soil testing is conducted to determine the suitability of box piles.
- Driving the Piles: Box piles are driven into the ground using hydraulic hammers or vibratory drivers. This ensures they reach the desired depth and soil layer.
- Filling and Reinforcement: Depending on the design, the hollow interior of the box pile may be filled with concrete or another reinforcing material.
- Final Adjustments: The tops of the piles are trimmed to the required level, and any necessary connections to the structure are made.
Factors to Consider When Using Box Piles
To maximize the benefits of box piles, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Soil Type: Conduct thorough soil analysis to ensure compatibility with box piles.
- Load Requirements: Determine the load-bearing capacity needed for your project.
- Material Quality: Use high-quality materials to ensure durability and performance.
- Environmental Conditions: Account for factors like water levels, corrosion risks, and seismic activity.
Why Choose Box Piles Over Traditional Piles?
While traditional piles like circular or H-piles have their merits, box piles offer distinct advantages in certain scenarios. Their hollow design allows for customization and adaptability, making them a more efficient choice for projects requiring precise load distribution or installation in challenging terrains.
Conclusion
Box piles are a cornerstone of modern construction, providing the strength and stability needed for a variety of projects. Their unique design, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make them a preferred choice for engineers and builders worldwide. Whether you’re planning a massive infrastructure project or a modest residential build, understanding the role of box piles can help you make informed decisions and achieve long-lasting results.