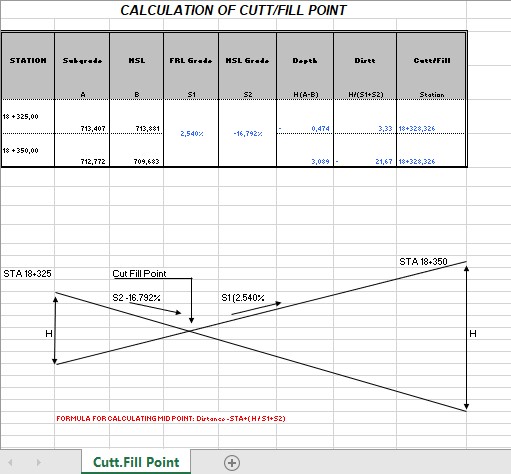
Calculation Of Cut and Fill Point Road Design Spreadsheet
10 December 2022Table of Contents
Calculation Of Cut and Fill Point Road Design Spreadsheet
In road design and construction, achieving a balance between functionality, cost-efficiency, and environmental sustainability is paramount. One of the most critical processes in this endeavor is the concept of “cut and fill.” This essential technique ensures that roads are built on stable, level terrain while minimizing waste and environmental impact. In this article, we delve into what cut and fill entails, its importance in road design, and how modern practices optimize its implementation.
What Is Cut and Fill?
Cut and fill is a grading technique used to create a level base for roads, railways, or other infrastructure projects. The process involves:
- Cut: Removing soil, rock, or other materials from elevated areas to lower the ground level.
- Fill: Using the removed material to raise low-lying areas, creating a balanced and even surface.
The objective is to achieve a uniform grade along the road alignment while minimizing the volume of imported or wasted material. By balancing the cut and fill quantities, construction teams can reduce costs and environmental disturbances.
Why Is Cut and Fill Important in Road Design?
- Economic Efficiency
- Reducing the need to transport materials offsite lowers costs associated with fuel, labor, and disposal.
- Using onsite materials for fill minimizes the need for expensive imported aggregates.
- Structural Integrity
- Properly executed cut and fill operations ensure that roads rest on stable, well-compacted soil, reducing the risk of subsidence or collapse.
- Environmental Considerations
- Minimizing material movement reduces the carbon footprint of construction activities.
- Careful planning ensures minimal disruption to natural landscapes and ecosystems.
- Adaptability to Terrain
- Roads often traverse varying topography, and cut and fill enable the design to adapt seamlessly, ensuring smooth and safe gradients.
The Process of Cut and Fill
1. Site Analysis
Before any grading begins, engineers conduct a thorough survey of the site. This includes:
- Topographical surveys to map elevation changes.
- Soil testing to determine load-bearing capacity and compaction requirements.
2. Design Planning
Using the survey data, engineers create a road profile that balances cuts and fills. Specialized software like AutoCAD Civil 3D or Bentley OpenRoads helps in visualizing and calculating earthwork volumes.
3. Excavation and Filling
- Cut: Heavy machinery like excavators and bulldozers remove high points along the road alignment. Rock blasting may be necessary for harder terrain.
- Fill: The excavated material is transported to low areas, where it is layered and compacted to ensure stability.
4. Compaction
Compaction is vital for preventing future settlement. Rollers or vibratory compactors are used to achieve the desired density.
5. Drainage Management
Proper drainage systems are integrated to prevent erosion and waterlogging, which can undermine the road structure.
Modern Innovations in Cut and Fill
- 3D Modeling and Drones Advanced 3D modeling software and drone surveys allow for precise measurements and visualizations, reducing errors and waste.
- Sustainable Practices
- Recycling existing materials, such as concrete or asphalt, for use as fill material.
- Incorporating erosion control measures like geotextiles and vegetation.
- Automated Machinery GPS-guided machinery ensures exact cuts and fills, improving accuracy and efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions
Challenge: Unstable Soil
Unstable or weak soils may require additional stabilization measures, such as lime or cement treatment.
Challenge: Environmental Regulations
Strict environmental laws necessitate careful planning to avoid habitat destruction and water contamination. Solutions include:
- Conducting environmental impact assessments.
- Adopting eco-friendly construction techniques.
Challenge: Weather Conditions
Rain or extreme temperatures can delay operations and affect soil compaction. Using weather-resistant materials and scheduling work during favorable conditions can mitigate these issues.
Conclusion
Cut and fill is more than just a construction technique—it’s a cornerstone of efficient and sustainable road design. By balancing the removal and placement of earth materials, engineers can create safe, durable, and environmentally responsible roadways. With advancements in technology and a focus on sustainability, the future of cut and fill promises even greater precision and efficiency, paving the way for innovative infrastructure projects worldwide.
Whether you’re a civil engineer, contractor, or simply curious about road construction, understanding the nuances of cut and fill provides valuable insight into the intricate art and science behind building the roads we travel every day.