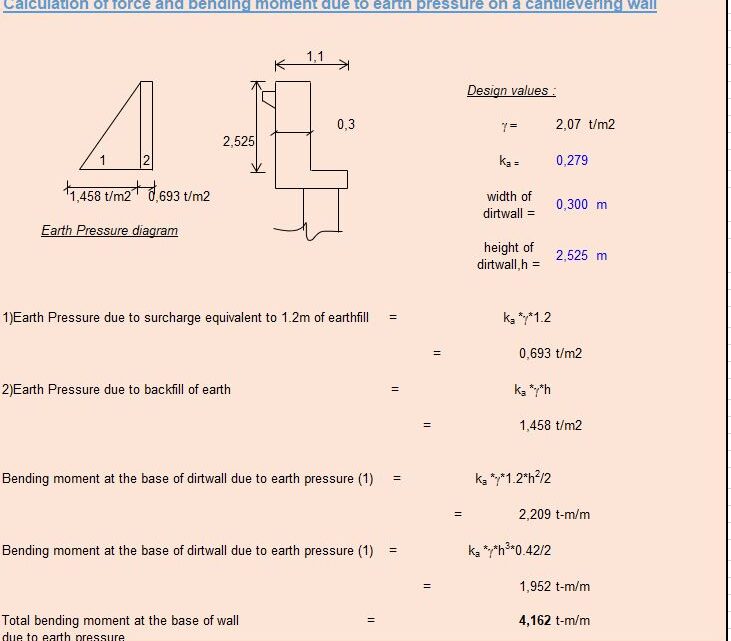
Calculation Of Force And Bending Moment Due to Earth Pressure On a Cantilevering Wall Spreadsheet
11 January 2025Table of Contents
Calculation Of Force And Bending Moment Due to Earth Pressure On a Cantilevering Wall Spreadsheet
Cantilever retaining walls are a fundamental element in modern construction, providing an efficient and durable solution for retaining soil in various applications. Known for their structural efficiency and aesthetic appeal, these walls are widely used in both residential and commercial projects. This guide explores the definition, components, advantages, design considerations, and construction methods of cantilever retaining walls, making it an essential resource for engineers, architects, and construction professionals.
What is a Cantilever Retaining Wall?
A cantilever retaining wall is a freestanding structure designed to retain soil or other materials. It operates on the principle of leverage, with a large base slab providing stability against lateral earth pressure. The wall consists of a thin vertical stem and a broad footing divided into two parts: the heel (extending beneath the retained material) and the toe (projecting outward on the opposite side).
Components of a Cantilever Retaining Wall
The primary components of a cantilever retaining wall include:
- Stem
- The vertical portion that retains the soil.
- Base Slab
- Comprises the heel and toe, distributing the load and ensuring stability.
- Shear Key
- A feature embedded in the base slab to resist sliding forces.
- Counterforts (Optional)
- Vertical bracing elements attached to the stem to enhance stability for higher walls.
- Drainage System
- Includes weep holes and filters to prevent water accumulation and reduce hydrostatic pressure.
Applications of Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever retaining walls are versatile and commonly used in various scenarios, including:
- Highways and Roads
- Retaining soil to create level surfaces for road construction.
- Residential Projects
- Supporting garden terraces or landscaping features.
- Commercial and Industrial Sites
- Providing structural support for buildings constructed on sloped terrains.
- Bridges
- Retaining abutments and wing walls.
- Erosion Control
- Stabilizing slopes to prevent soil erosion in hilly or coastal regions.
Advantages of Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Cost-Effective for Moderate Heights
- Ideal for walls up to 6 meters (20 feet) tall, offering a balance between cost and efficiency.
- Efficient Use of Materials
- Utilizes concrete and steel reinforcement effectively, reducing material waste.
- Aesthetic Versatility
- Can be customized with various finishes to blend with surrounding landscapes.
- Durability
- Designed to withstand lateral earth pressure and environmental forces for decades.
- Space Optimization
- Requires less horizontal space compared to gravity retaining walls.
Design Considerations for Cantilever Retaining Walls
Designing a cantilever retaining wall requires careful analysis of various factors to ensure stability and functionality. Key considerations include:
- Soil Properties
- Understanding soil type, cohesion, and angle of internal friction is critical for stability.
- Lateral Earth Pressure
- Calculating active, passive, and at-rest pressures to determine wall dimensions.
- Foundation Stability
- Ensuring the base slab resists sliding, overturning, and bearing capacity failures.
- Drainage Provisions
- Including drainage layers, weep holes, and filters to minimize water pressure.
- Reinforcement Design
- Ensuring adequate steel reinforcement in the stem and base slab to handle bending moments and shear forces.
- Environmental Factors
- Accounting for seismic loads, frost action, and corrosion potential in design.
Construction Process for Cantilever Retaining Walls
Building a cantilever retaining wall involves several steps:
1. Site Preparation
- Clear the site of debris and level the area for foundation excavation.
2. Excavation
- Excavate the foundation trench to the required depth, ensuring a firm base.
3. Formwork Installation
- Set up formwork for the stem and base slab according to the design specifications.
4. Reinforcement Placement
- Place steel reinforcement bars in the stem and base slab, ensuring proper alignment and spacing.
5. Concrete Pouring
- Pour high-quality concrete into the formwork and use vibrators to eliminate air pockets.
6. Curing
- Allow the concrete to cure for at least 7-14 days to achieve optimal strength.
7. Backfilling and Drainage Installation
- Backfill the retained side with compacted soil and install the drainage system to prevent water buildup.
Limitations of Cantilever Retaining Walls
While cantilever retaining walls offer numerous benefits, they have certain limitations:
- Height Restrictions
- Not suitable for heights exceeding 6 meters without counterforts or additional reinforcement.
- Complex Construction
- Requires skilled labor and precise execution to ensure stability and durability.
- High Initial Cost
- Although cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment may be higher compared to simpler wall types.
Conclusion
Cantilever retaining walls are a versatile and efficient solution for soil retention in various construction projects. By combining structural efficiency with aesthetic flexibility, these walls serve as a reliable choice for engineers and architects. Proper design, careful material selection, and skilled construction practices are essential to ensure the longevity and performance of cantilever walls.
Whether you’re stabilizing a slope, building a terrace, or supporting a roadway, cantilever retaining walls offer a durable and cost-effective solution. Incorporating this method into your construction projects can lead to safer and more sustainable infrastructure.


