Design and Calculation Of Bearing Pad Spreadsheet
28 January 2022Design and Calculation Of Bearing Pad Spreadsheet
In the ever-evolving world of construction, the importance of small yet significant components often goes unnoticed. One such vital element is the bearing pad. These seemingly simple materials play a crucial role in ensuring structural stability, durability, and performance across various construction projects. This article delves into what bearing pads are, their types, benefits, and applications in construction.
What is a Bearing Pad?
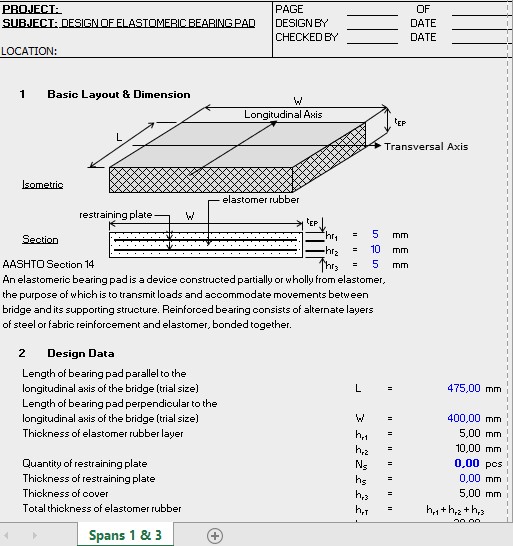
A bearing pad is a component used in construction to distribute loads and absorb stresses between structural elements. Typically placed between beams, girders, or columns and their supporting structures, bearing pads help to minimize stress concentrations and allow for controlled movement due to factors such as temperature changes, dynamic loads, and structural deflection.
Types of Bearing Pads
Bearing pads come in various types, each tailored for specific applications and structural requirements. Below are the most common types:
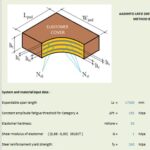
- Elastomeric Bearing Pads:
- Made from rubber (natural or synthetic) reinforced with steel plates or fibers.
- Known for their flexibility and durability, these pads can accommodate vertical loads and horizontal movements while resisting deformation.
- Neoprene Bearing Pads:
- A specific type of elastomeric pad made from neoprene, offering excellent resistance to weather, ozone, and chemicals.
- Ideal for use in bridges, parking structures, and other exposed environments.
- Sliding Bearing Pads:
- Feature a low-friction surface that allows for significant horizontal movement.
- Commonly used in structures subject to large thermal expansions, such as long-span bridges.
- Teflon-Coated Bearing Pads:
- Incorporate a Teflon layer for enhanced movement capabilities.
- Suitable for applications requiring low friction and high load-bearing capacity.
- Cotton Duck Pads:
- Comprised of layers of cotton fabric impregnated with rubber.
- Designed for heavy loads and high-pressure environments, such as industrial machinery foundations.
Benefits of Bearing Pads
Bearing pads offer numerous benefits that make them indispensable in modern construction. These include:
- Load Distribution:
- Prevents stress concentrations by evenly distributing loads across structural elements.
- Movement Accommodation:
- Allows for thermal expansion, contraction, and other movements without causing damage.
- Vibration Isolation:
- Absorbs vibrations and shocks, enhancing structural comfort and longevity.
- Durability:
- Resistant to wear, environmental factors, and chemical exposure, ensuring a long service life.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Reduces maintenance and repair costs by mitigating structural stress and damage.
Applications of Bearing Pads in Construction
Bearing pads are versatile and find applications in various construction scenarios, including:
- Bridges:
- Used to support bridge girders and accommodate thermal and dynamic movements.
- Buildings:
- Installed in multi-story structures to isolate vibrations and distribute loads between floors.
- Industrial Foundations:
- Provide a stable base for heavy machinery, reducing vibrations and improving operational efficiency.
- Railway Tracks:
- Enhance track stability and reduce noise and vibration caused by train movements.
- Highway Structures:
- Used in overpasses, underpasses, and retaining walls to ensure stability and flexibility.
Key Considerations When Choosing Bearing Pads
Selecting the right bearing pad is crucial for the success of any construction project. Here are some factors to consider:
- Load Capacity:
- Determine the vertical and horizontal loads the pad must support.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Consider factors such as temperature variations, chemical exposure, and weather conditions.
- Movement Requirements:
- Assess the extent of movement (expansion, contraction, rotation) the structure will experience.
- Material Durability:
- Ensure the pad material is suitable for the specific application and environment.
- Compliance with Standards:
- Verify that the bearing pad meets relevant industry standards and regulations.
Conclusion
Bearing pads may be small in size, but their impact on construction projects is monumental. By ensuring load distribution, accommodating movement, and enhancing structural durability, these essential components contribute significantly to the safety and longevity of bridges, buildings, and other structures. Choosing the right type of bearing pad tailored to your project’s requirements can make all the difference in achieving structural excellence.
For construction professionals and engineers, understanding the role and functionality of bearing pads is key to designing resilient and cost-effective structures. Whether you’re working on a bridge, a high-rise building, or an industrial foundation, investing in high-quality bearing pads ensures a solid foundation for success.