Design Of RC Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footing Spreadsheet
28 February 2025Table of Contents
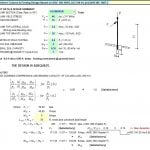
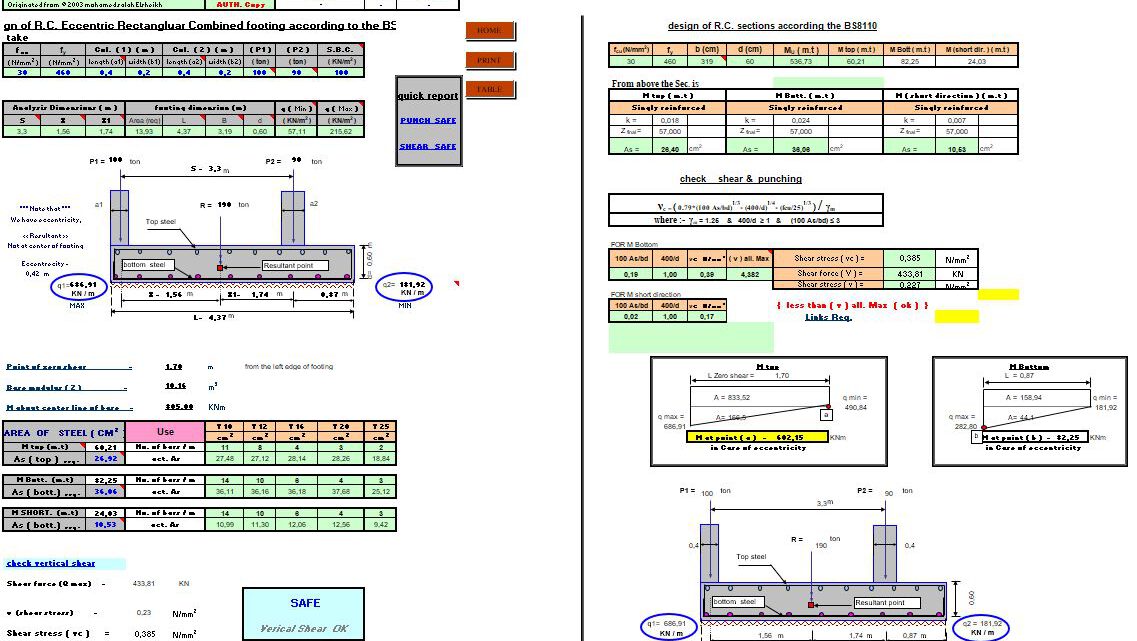
Design Of RC Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footing Spreadsheet
An RC eccentric rectangular combined footing is a reinforced concrete footing designed to support two or more columns with unequal loads or columns located at the edge of a property line. The term “eccentric” refers to the fact that the resultant load does not pass through the centroid of the footing, leading to uneven load distribution.
These footings are typically rectangular in shape and are reinforced to handle bending moments and shear forces caused by the eccentricity. They are widely used in urban construction, where space constraints require placing columns close to property boundaries.
Why Use Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footings?
Eccentric rectangular combined footings are used in the following scenarios:
- Property Line Constraints: When columns are placed near property lines, conventional isolated footings would extend beyond the boundary, making combined footings a suitable alternative.
- Unequal Load Distribution: When columns carry unequal loads, combined footings effectively distribute the pressure on the soil.
- Economical Solution: They are more cost-effective than using separate isolated footings for closely spaced columns.
- Structural Stability: The combined footing ensures structural stability by preventing differential settlement.
Design Principles of Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footings
Designing an eccentric rectangular combined footing involves several critical considerations:
1. Load Analysis
Calculate the loads acting on each column, including dead loads (self-weight) and live loads (e.g., people, furniture, and equipment). Consider wind and seismic loads if applicable.
2. Eccentricity Calculation
Determine the eccentricity by calculating the distance between the resultant load’s line of action and the centroid of the footing. This eccentricity induces bending moments that must be accounted for in the design.
3. Size and Shape of Footing
The footing is typically rectangular, with its length and width designed to ensure that the resultant pressure is uniformly distributed over the soil.
4. Pressure Distribution
Check for soil bearing capacity to ensure that the pressure under the footing is within safe limits. An eccentric load results in a non-uniform pressure distribution.
5. Bending Moment and Shear Force Analysis
Calculate the bending moments and shear forces caused by the eccentric loading. Design the reinforcement to resist these forces.
6. Reinforcement Details
- Longitudinal Reinforcement: Provided along the length of the footing to resist bending moments.
- Transverse Reinforcement: Placed along the width to handle shear forces.
- Top Reinforcement: Required to resist negative moments at the fixed end of the columns.
7. Check for Stability and Safety
Ensure stability against overturning, sliding, and bearing failure. Follow standard codes such as ACI, IS, or Eurocode for safety requirements.
Construction Method for RC Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footing
Constructing an eccentric rectangular combined footing involves the following steps:
-
Site Preparation and Excavation
Clear the site and excavate the soil according to the dimensions of the combined footing. Ensure that the excavation is level and compact the soil to achieve the required bearing capacity. -
Formwork Installation
Install sturdy formwork to shape the concrete. The formwork must be precisely aligned to maintain the required eccentricity. -
Placement of Reinforcement
- Place longitudinal and transverse reinforcement bars as per the design specifications.
- Provide additional top reinforcement at the fixed end of the columns to resist negative moments.
- Ensure proper anchorage and lap length for reinforcement continuity.
-
Concrete Pouring and Compaction
Pour high-strength concrete and compact it using vibrators to eliminate air pockets. Proper compaction ensures uniform strength and durability. -
Curing
Cure the concrete for at least 7 days to achieve the desired strength and prevent shrinkage cracks. -
Formwork Removal and Backfilling
Remove the formwork carefully after the concrete has gained adequate strength. Backfill the excavated area with soil and compact it properly.
Advantages of RC Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footings
- Efficient Space Utilization: Ideal for urban construction where space constraints exist.
- Economical Design: Cost-effective compared to isolated footings for closely spaced columns.
- Structural Stability: Distributes uneven loads effectively, preventing differential settlement.
- Versatility: Suitable for various building types, including residential, commercial, and industrial structures.
Disadvantages of RC Eccentric Rectangular Combined Footings
- Complex Design and Analysis: Requires accurate load calculations and eccentricity analysis.
- High Reinforcement Requirement: More reinforcement is needed to handle bending moments and shear forces.
- Challenging Construction: Precise formwork alignment and reinforcement placement are essential.
- Higher Cost for High Loads: Cost increases with higher loads and larger eccentricity values.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring Eccentricity Effects: Can lead to uneven pressure distribution and potential structural failure.
- Inadequate Reinforcement: May cause bending or shear failure under high loads.
- Improper Formwork Alignment: Results in incorrect eccentricity and misalignment of columns.
- Poor Quality Concrete: Affects the durability and load-bearing capacity of the footing.