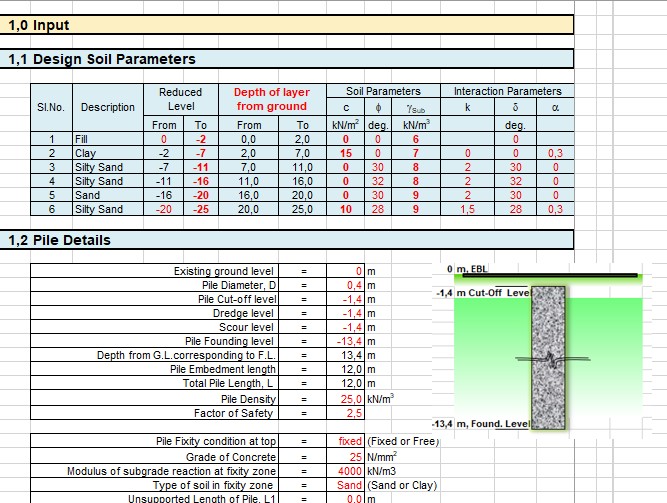
Pile Capacity All Calculations Spreadsheet
1 February 2025Table of Contents
Pile Capacity All Calculations Spreadsheet
Pile foundations are a crucial element in construction, providing stability and load-bearing capacity for structures built on weak or variable soils. Determining pile capacity is essential for ensuring the safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness of a project. This article explores the concept of pile capacity, its types, influencing factors, calculation methods, and best practices.
What Is Pile Capacity?
Pile capacity refers to the maximum load a pile foundation can support without experiencing failure. It consists of two main components:
- End Bearing Capacity: The load carried by the pile’s tip, which transfers forces directly to a strong soil or rock layer.
- Skin Friction Capacity: The load resisted along the pile’s surface due to friction between the pile and the surrounding soil.
Types of Pile Foundations
- End-Bearing Piles: These piles transfer loads directly to a firm stratum, such as rock or dense soil.
- Friction Piles: These rely on skin friction to distribute loads through weaker soils.
- Combination Piles: These utilize both end-bearing and friction resistance for enhanced load support.
Factors Affecting Pile Capacity
Several factors influence the pile capacity in construction, including:
- Soil Properties: The type, density, and cohesion of the soil affect how much load the pile can bear.
- Pile Material: Concrete, steel, and timber piles have different strength and load-bearing characteristics.
- Pile Length and Diameter: Longer and wider piles distribute loads more effectively.
- Installation Method: Driven, bored, or screw piles behave differently under loads.
- Water Table Level: High groundwater can reduce effective stress and impact pile performance.
How to Calculate Pile Capacity
Pile capacity is typically determined using analytical methods, field tests, or empirical formulas. The most common approaches include:
1. Static Formula Method
The ultimate load capacity (Qu) is given by:
Qu = Qb + Qs
Where:
- Qb = End bearing capacity
- Qs = Skin friction capacity
For end-bearing capacity:
Qb = Ab × qb
Where:
- Ab = Cross-sectional area of the pile tip
- qb = Ultimate bearing capacity of soil at the pile tip
For skin friction:
Qs = ∑(Asi × fsi)
Where:
- Asi = Surface area of each pile segment
- fsi = Unit skin friction of soil
2. Pile Load Tests
- Static Load Test: Measures settlement under an applied load.
- Dynamic Load Test: Assesses pile behavior using hammer impact.
- Pile Integrity Test: Evaluates defects in pile structure.
Best Practices for Optimizing Pile Capacity
- Conduct thorough geotechnical investigations before pile installation.
- Choose the appropriate pile type and material for the specific site conditions.
- Use proper installation techniques to minimize soil disturbance and improve capacity.
- Perform load testing to validate theoretical calculations.
- Regularly inspect and maintain piles to prevent long-term structural issues.
Conclusion
Understanding pile capacity is essential for designing safe and stable foundations in construction. By considering soil conditions, pile material, and calculation methods, engineers can optimize pile performance and ensure the long-term success of a project. Proper assessment and testing of pile capacity help mitigate risks, reduce construction costs, and enhance structural integrity.