Spiral Column Reinforcement Design Spreadsheet
17 December 2021Table of Contents
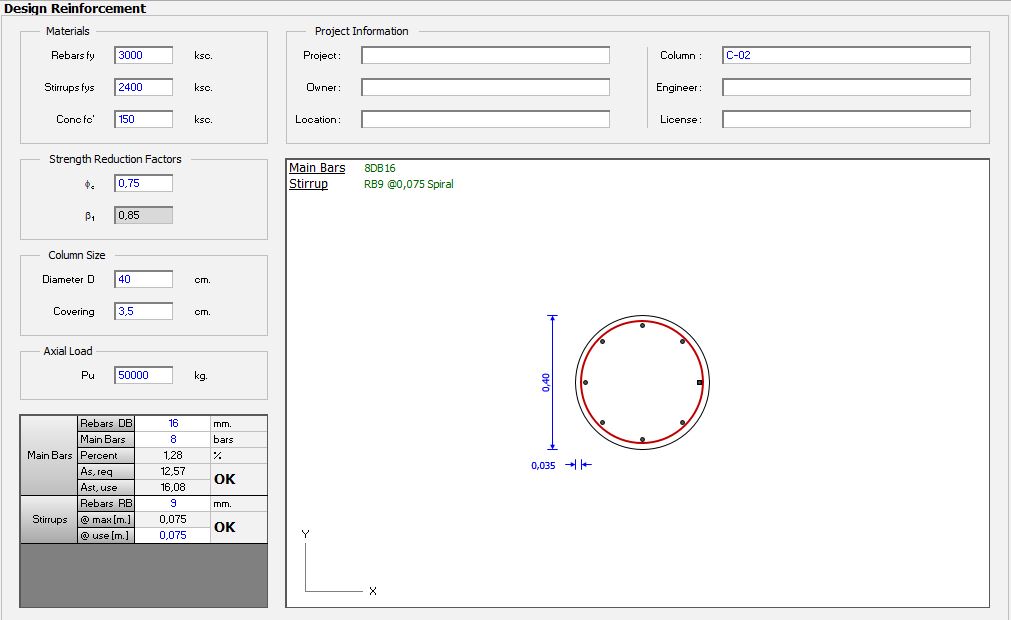
Spiral Column Reinforcement Design Spreadsheet
Structural integrity is the backbone of any construction project, and when it comes to reinforced concrete columns, choosing the right reinforcement method is critical. Among various techniques, spiral column reinforcement stands out for its superior strength, durability, and seismic resistance. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits, applications, and design considerations of spiral column reinforcement and share a free activation for personal use to elevate your construction projects.
What is Spiral Column Reinforcement?
Spiral column reinforcement is a type of lateral reinforcement where steel bars are shaped into continuous spirals around a column’s vertical reinforcement. These spirals, also known as helical ties, serve to confine the core concrete, enhancing its strength and ductility.
This reinforcement technique is commonly used in heavily loaded structures and seismic zones, where the risk of collapse is high without proper confinement.
Key Benefits of Spiral Column Reinforcement
- Enhanced Strength: Spiral reinforcement significantly improves the compressive strength of concrete columns, making them more resilient under heavy loads.
- Seismic Resistance: The confinement provided by the spirals enhances ductility, allowing columns to absorb and dissipate seismic energy effectively.
- Crack Prevention: The uniform distribution of spiral ties minimizes the risk of cracking, even under extreme stress conditions.
- Improved Load Distribution: Spirals ensure better load transfer between the core and outer layers of concrete, enhancing overall structural performance.
- Durability: With superior resistance to external forces, spiral-reinforced columns maintain their structural integrity for longer periods, reducing maintenance costs.
Applications of Spiral Column Reinforcement
Spiral column reinforcement is ideal for:
- High-Rise Buildings: Ensuring structural stability under vertical and lateral loads.
- Bridges and Overpasses: Providing durability and resilience against dynamic forces.
- Industrial Structures: Supporting heavy equipment and machinery.
- Seismic Zones: Enhancing safety in earthquake-prone areas.
- Parking Garages: Withstanding vehicular loads and impacts.
Design Considerations
When designing columns with spiral reinforcement, several factors should be considered:
- Spiral Diameter and Pitch: The diameter and spacing of the spirals affect confinement effectiveness. Industry standards recommend a pitch of 1/6th to 1/10th of the column diameter.
- Material Selection: High-quality steel should be used for the spirals to ensure durability and strength.
- Concrete Strength: The core concrete’s properties should complement the reinforcement for optimal performance.
- Compliance with Codes: Adherence to building codes and standards, such as ACI 318, is crucial for safety and reliability.


